AMF Configuration and Client objects
To use AMF you need an AMFConfiguration object.
This immutable object stores and configures:
- Parsing options
- Render options
- Resource loaders
- Plugins
- Transformation pipelines
- Validation profiles
- Error handler providers
- Event Listeners
- And more ...
The AMF configuration object provides an AMF Client that you'll use to interact with AMF.
AMF Configuration
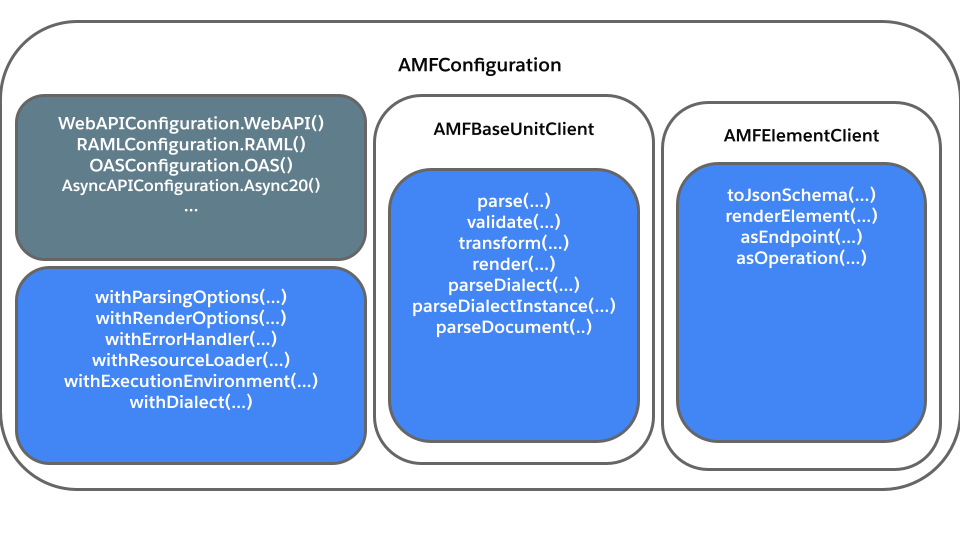
Configuration types
The AMFConfiguration class has a builder style setup so that you can create a configuration according to your project needs.
AMF already provides specific and general configurations.
Specific configurations
AMF has predefined configurations for each specification it supports:
RAMLConfigurationRAMLConfiguration.RAML08()for RAML 0.8 documentsRAMLConfiguration.RAML10()for RAML 1.0 documents
OASConfigurationOASConfiguration.OAS20()for OAS 2.0 documentsOASConfiguration.OAS30()for OAS 3.0 documents
AsyncAPIConfigurationAsyncAPIConfiguration.Async20()for AsyncAPI 2.0.0 documents
Each configuration has all it needs to parse, transform, validate and render documents.
General configurations
AMF also has general-purpose configurations that support spec-agnostic parsing. This enables parsing without knowing the exact specification of a document, but all other operations (transformation, validation, rendering) are spec-dependent and require a specific configuration. These general-purpose configurations are:
RAMLConfiguration.RAML()can parse both RAML 0.8 and RAML 1.0 documentsOASConfiguration.OAS()can parse both OAS 2.0 and OAS 3.0 documentsWebAPIConfiguration.WebAPI()can parse RAML and OAS documentsAPIConfiguration.API()can parse RAML, OAS and AsyncAPI documents
The AMFParseResult returned by parsing contains the exact specification parsed in the property .sourceSpec, and each configuration
has the method .fromSpec(Spec) that returns the specific specific configuration for the spec provided,
so it's simple to use a general-purpose configuration and then use it to get the specific configuration needed.
AMF Client
To interact with AMF you need to create a client from a configuration. There are 2 types of clients in AMF, depending on what you want to work with:
baseUnitClient- Contains common AMF operations to operate with
BaseUnit- A
BaseUnitis the model used by AMF to store parsed documents
- A
- Contains methods like
parse(url),parseContent(string),transform(BaseUnit),render(BaseUnit),validate(BaseUnit), etc.
- Contains common AMF operations to operate with
elementClient- Contains functionality associated with specific elements of the AMF graph model, not documents.
- Contains methods like
getPayloadValidatorFor(shape, mediatype, mode),toJsonSchema(element),toRamlDatatype(element)
The following code is an example of creating a configuration, a client, and using AMF:
- Scala
- Java
- TypeScript
import amf.apicontract.client.scala.RAMLConfiguration
val configuration = RAMLConfiguration.RAML10()
val client = configuration.baseUnitClient()
// your code...
import amf.apicontract.client.platform.OASConfiguration;
import amf.apicontract.client.platform.AMFBaseUnitClient;
class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
final AMFConfiguration configuration = OASConfiguration.OAS30();
final AMFBaseUnitClient client = configuration.baseUnitClient();
// your code...
}
}
import {
AMFBaseUnitClient,
AMFConfiguration,
OASConfiguration,
} from "amf-client-js";
const configuration: AMFConfiguration = OASConfiguration.OAS20()
const client: AMFBaseUnitClient = configuration.client
// ... your code